Obsession: Separation Anxiety
Written by: Hong Kong Registered Psychologist, Ching Wai Keung
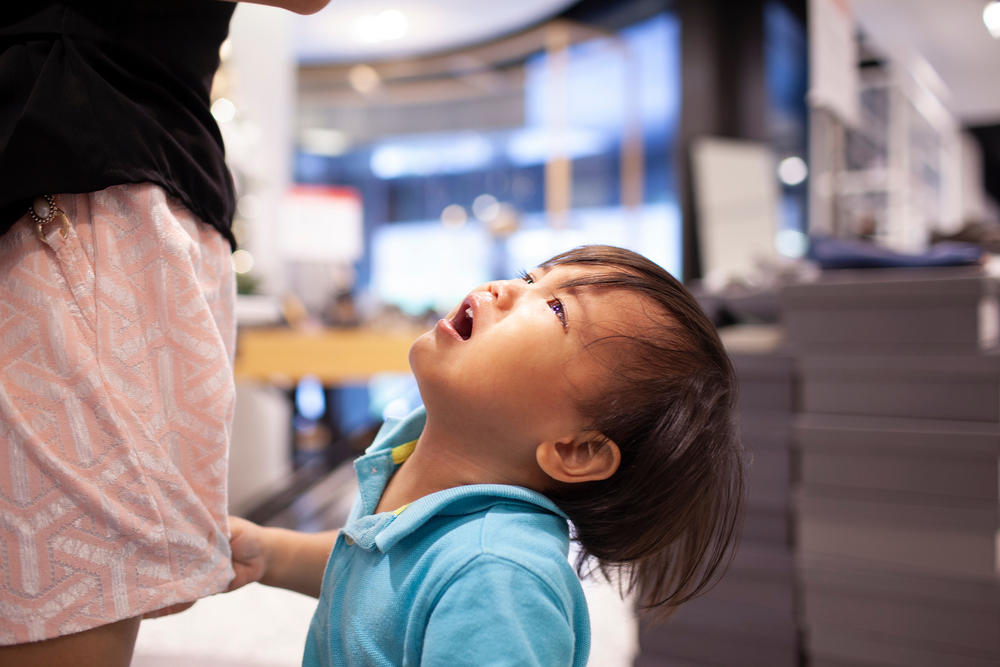
Around nine months of age, babies become unusually clingy. Even if the mother goes to the bathroom, the baby may appear extremely anxious, clinging tightly to the mother and even crying loudly.
Separation anxiety can lead to two different types of reactions. In some cases, when separated from the caregiver, the baby will exhibit attachment-seeking behaviors, such as clinging to the mother, trying every possible way to find the mother, or crawling wherever the mother goes (Ainsworth, Bell, & Stayton, 1971). Separation can also result in behaviors such as despair, resistance, and detachment, depending on the duration of the separation (Bowlby, 1960; Robertson & Robertson, 1989).
A child's reaction to separation can also change depending on the environment. For example, in a familiar home environment, the child will exhibit less anxiety compared to being in an unfamiliar environment (Ross, Kagan, Zelazo, & Kotelchuck, 1975).
Around seven months of age, the concept of object permanence begins to emerge in children. They understand that even if they cannot see someone or something, it does not mean that the person or object has disappeared. When children are able to establish this concept, their separation anxiety will relatively decrease. If the mother can frequently communicate with the child, express positive emotions and feelings towards the infant, and provide appropriate stimulation and assistance, the child will more easily grasp and apply the concept of object permanence to both objects and people (Chazan, 1981).
Helping children cope with separation anxiety requires a certain amount of time, allowing the child and caregiver to develop a close, attached emotional relationship (Attachment), and waiting for the child's own development to mature before it can be effective. For a two-year-old child, they can use photographs to alleviate their feelings of sorrow when separated from their caregiver (Passman & Longeway, 1982); a three-year-old child can even stay overnight at their grandparents' house without their parents being present.
Whether a child can develop this kind of "resilience" depends on whether the caregiver and the child can establish a close emotional relationship. Once the mutual relationship is established, the child can soothe their anxiety caused by separation by imagining the image of their parents and recalling their parents' love (Development Through Life, Barbara M. Newman, Philip R. Newman, Wadsworth, 2003).